What are stem cells?
It is said that humans are made up of 60 trillion cells, and these cells are constantly being replaced behind the scenes in our bodies.
Just as humans have a lifespan, so do cells. Some cells, like those in the skin, are replaced from the cell membrane every six weeks and are excreted as dirt and dead skin cells. Other cells, like the nerve cells in the brain, are never replaced.
Stem cells are the source (stem) of the cells that make up our bodies. There are two types of stem cells: tissue stem cells and pluripotent stem cells.
Stem cells are found throughout the body, but are said to be particularly abundant in bone marrow and abdominal fat.
Because harvesting stem cells from bone marrow requires general anesthesia and is burdensome and risky, stem cells harvested from abdominal fat are commonly used.
Stem cells have the ability to divide and create identical cells, as well as to create organs and tissues in the body.
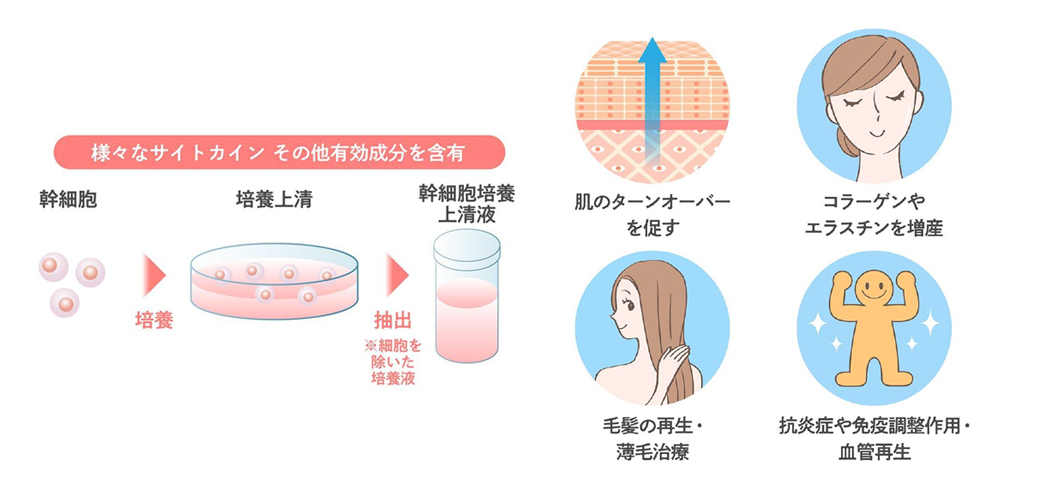
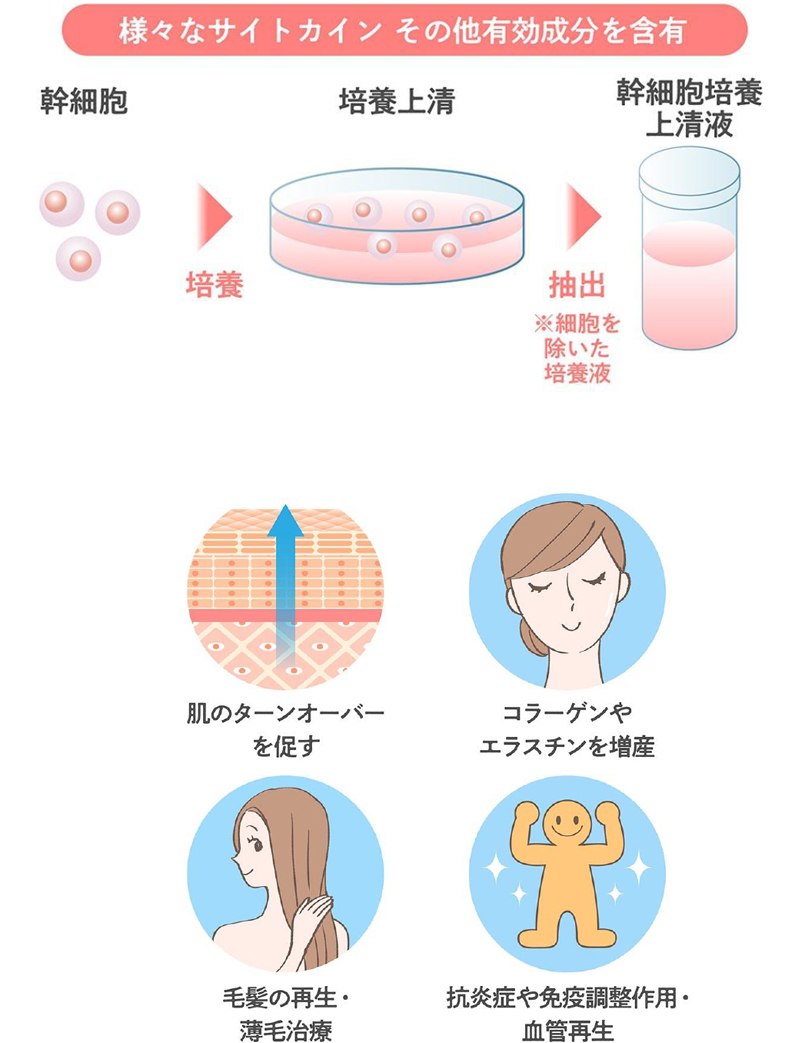
Stem cells are known for their extremely high regenerative capacity and are used in many treatments in regenerative medicine and cosmetic medicine, and the supernatant liquid from which these stem cells are cultured is used as a cosmetic ingredient.
In recent years, there has also been growing interest in exosomes, which are secreted during stem cell culture.
What are exosomes?
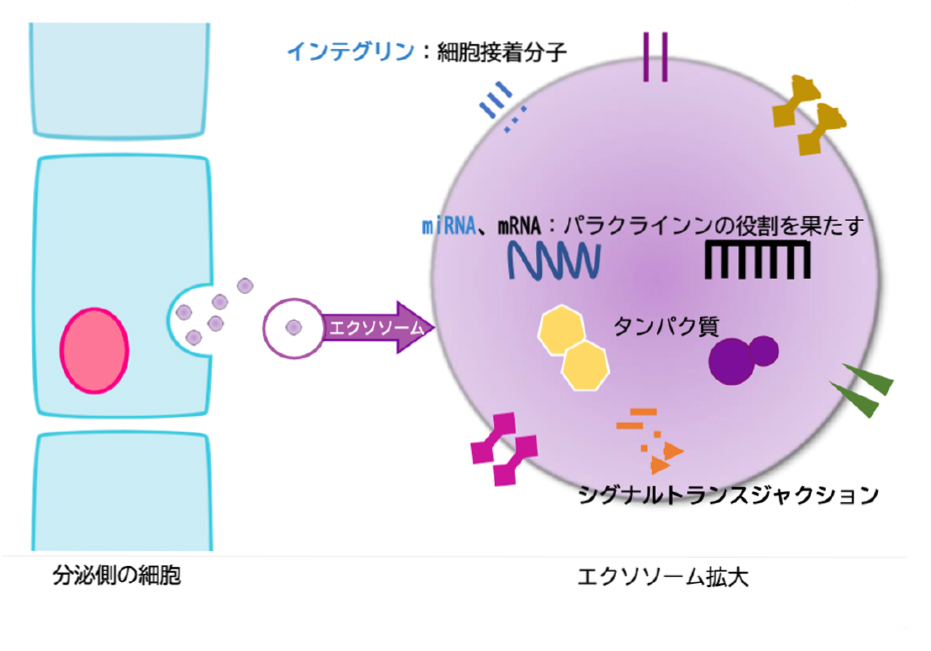
Exosomes are “very small capsules” measuring 30 to 150 nm that are secreted by cells.
They contain proteins, lipids, mRNA, miRNA, etc., which are used to exchange information between cells.
This allows them to activate the functions of other cells and deliver instructions that promote repair.
Exosome subcutaneous injection therapy
For patients who are hesitant about intravenous injections or afraid of needles, subcutaneous injections are performed using a needle-free syringe, which allows for safer injections.
Subcutaneous injections are performed using a highly safe needle-free syringe, the only one in Europe that is certified for intravesical administration of vaccines and medicines.
The device was equally effective in experiments with nanosuspensions, which have particles similar in size to exosomes, and can be injected without damaging the structure of exosomes.
Expected effects
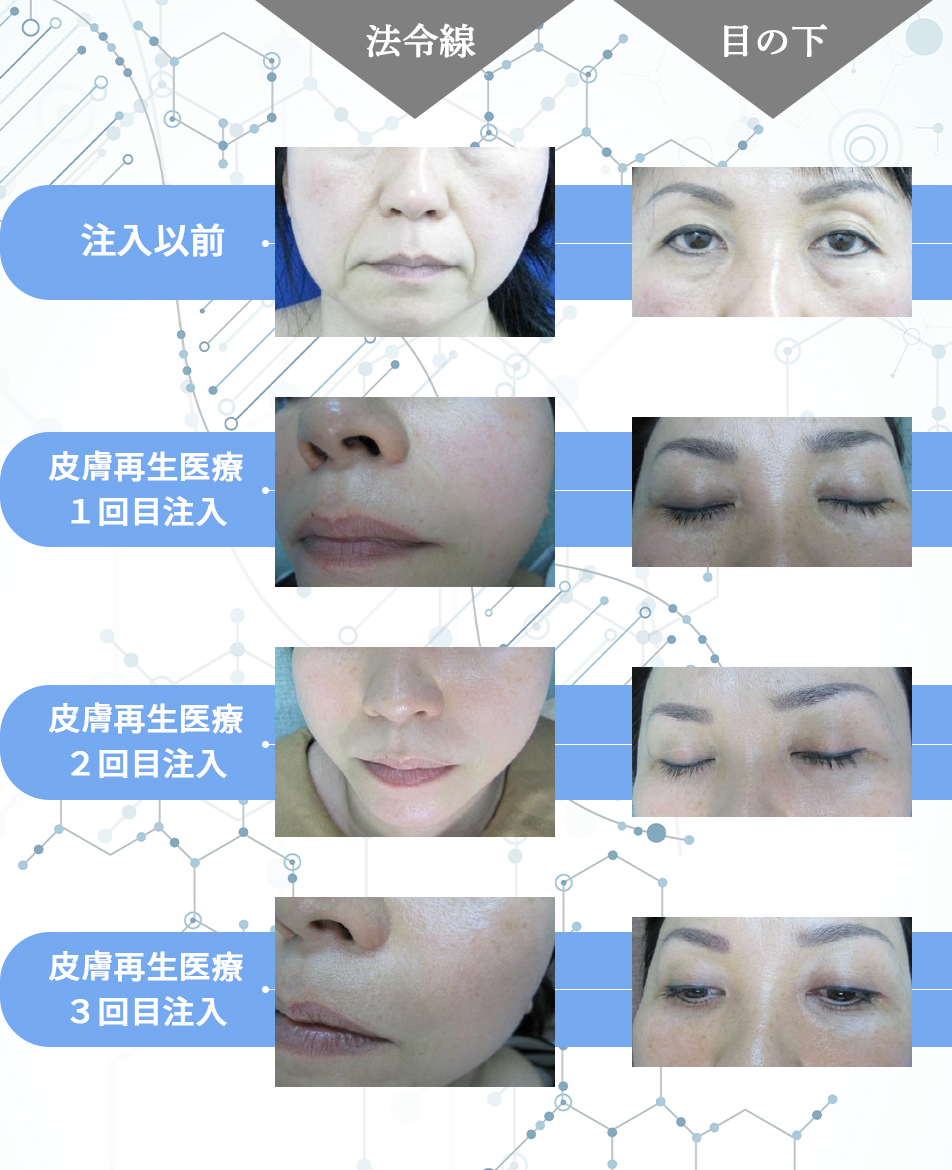
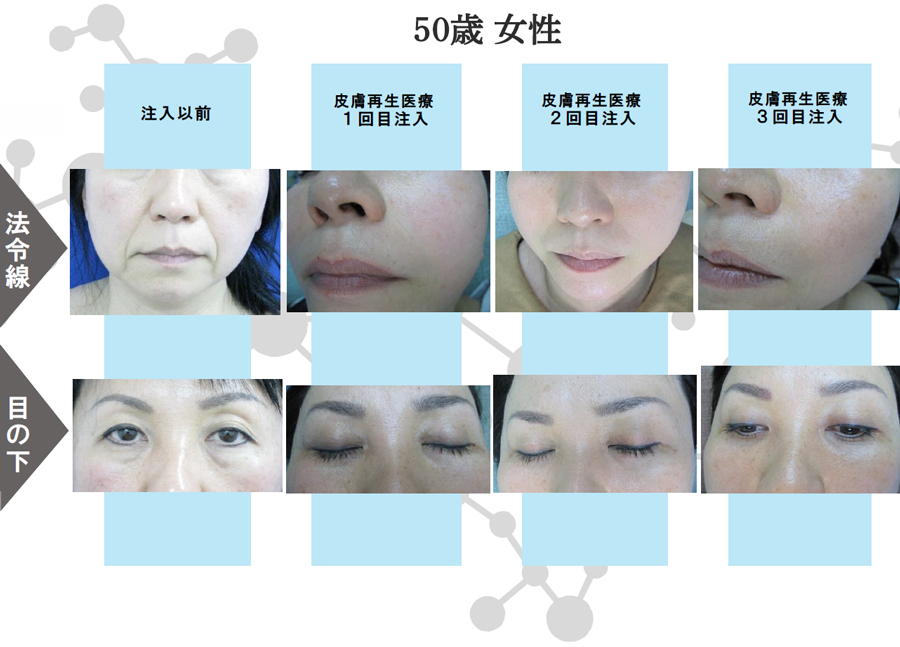
Exosomes have the effect of promoting and regulating skin turnover, and are expected to have a positive effect on a wide range of skin problems.
Skin problems such as dry skin are caused by disrupted turnover and a weakened barrier function, but exosomes can repair and improve this function, and are thought to be effective in maintaining healthy, beautiful skin.
Anti-aging effects such as tissue regeneration, wrinkle reduction, whitening, antioxidant properties, hair growth, and hair thickening are expected.
Treatment time and number of sessions
Approximately 1-2ml per use *Excluding saline solution Recommended once or multiple times depending on purpose
Safety of exosomes
Exosomes are expected to be a relatively safe treatment with fewer side effects than other treatments.
Because they are derived from human cells, there is a low risk of toxicity or rejection in the body.
Additionally, we conduct research and development at our group’s cell culture facilities to further improve and enhance cell culture technology and safety.
Regarding stem cells, we are engaged in joint development with partners, establishing cell culture protocols, researching and developing new processes, researching reagents, and supporting the skills development of cell culture technicians.
Types and characteristics of stem cells
Adipose tissue-derived stem cells Made from somatic cells
Features
・It is possible to easily extract large quantities of stem cells from subcutaneous fat tissue using techniques such as liposuction (approximately 100 to 1,000 times the amount of bone marrow stem cells).
・It is said that they also have the ability of bone marrow stem cells to differentiate into bone, fat, cartilage, etc.
Main functions of stem cells
Wound healing, differentiation, hair growth and hair growth, neovascularization, abundant production of proteins that promote cell activation, etc.
Umbilical cord-derived stem cells Collected from the umbilical cord
Features
・Umbilical cord blood is the blood that flows through the umbilical cord and placenta, and is said to have the greatest ability to develop cells in the body.
・They are known to be more active and have a higher proliferation capacity than adult stem cells (such as those from fat, dental pulp, and bone marrow).
Dental pulp-derived stem cells Taken from the nerve in the center of the tooth
Features
・The regenerative factors of dental pulp-derived stem cells are highly effective in many ways and have excellent proliferation capabilities.
・It can be taken from infants.
Main functions of stem cells
Wound healing, differentiation, hair growth and hair growth, neovascularization, abundant production of proteins that promote cell activation, etc.
Clinical
dermatitis treatment Autologous adipose-derived stem cell administration
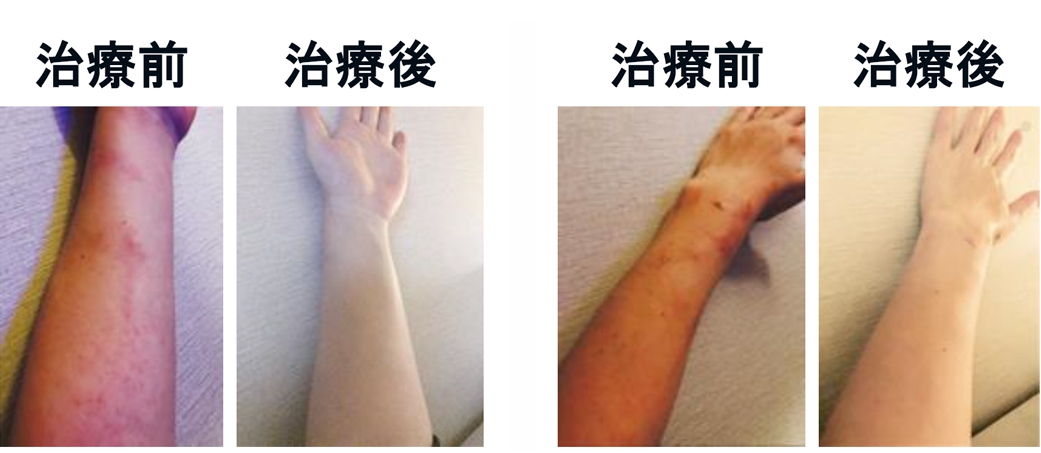
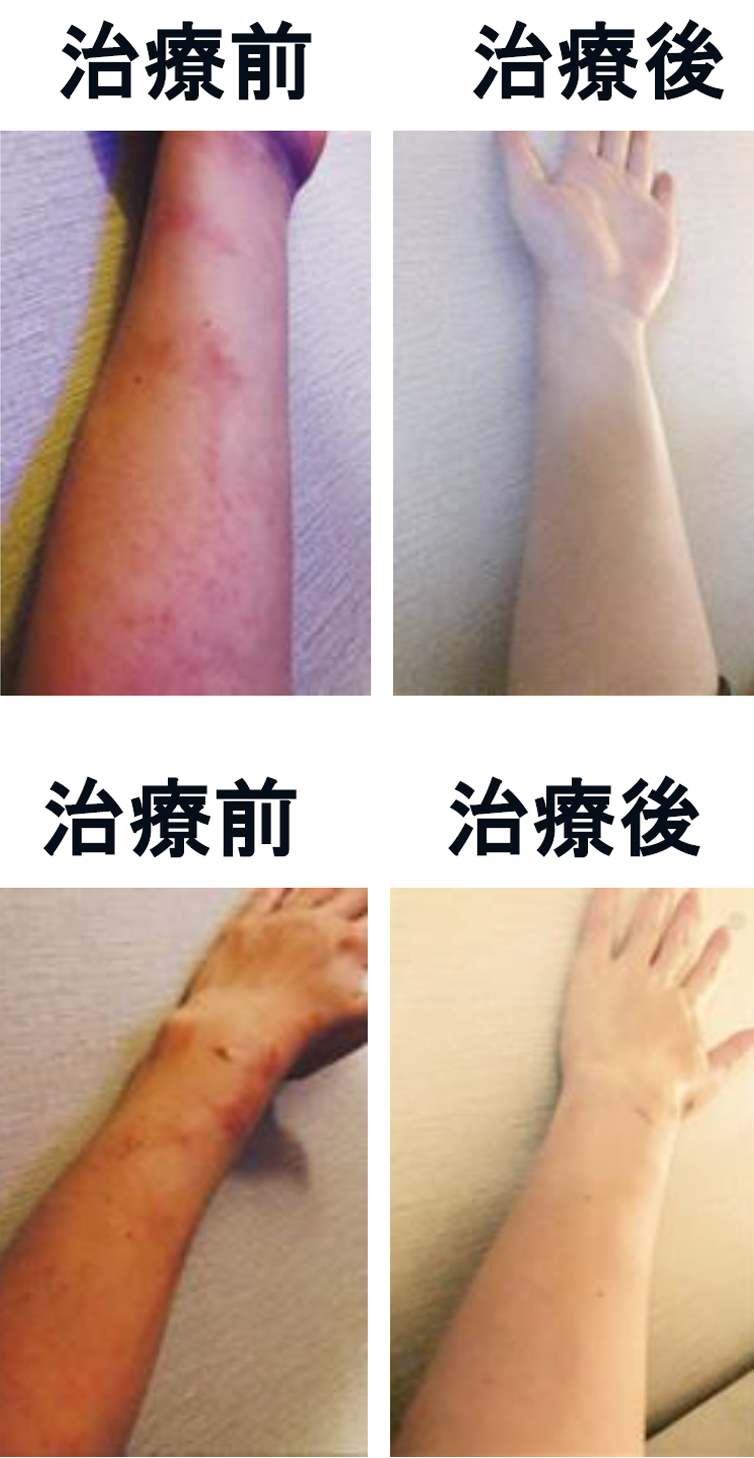
Beauty skin regeneration treatment Autologous adipose-derived stem cell administration
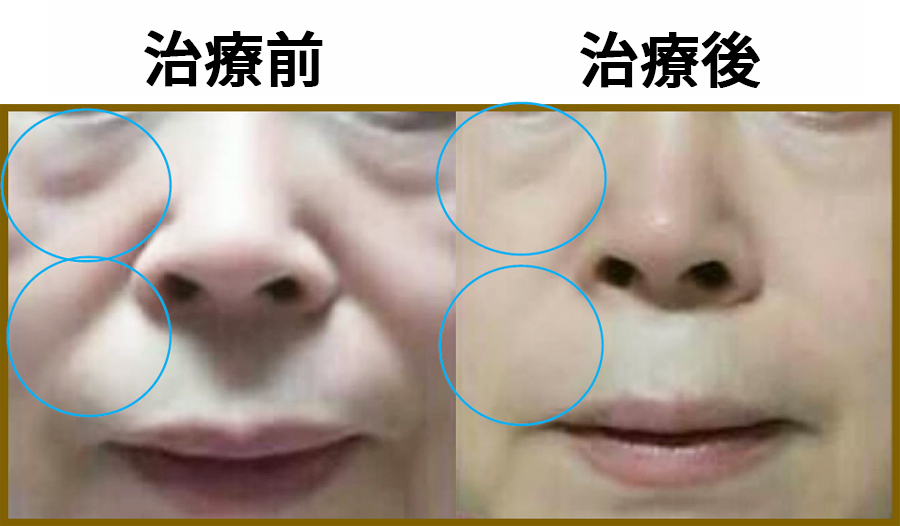
Improves blemishes, wrinkles, and sagging skin